PRTG Manual: NetApp SnapMirror Sensor
IMPORTANT INFORMATION |
|---|
This sensor supports NetApp cDOT as of version 8.3 or ONTAP from versions 9.0 to 9.12. If you use ONTAP as of version 9.6, we recommend that you use the NetApp SnapMirror v2 sensor. |
The NetApp SnapMirror sensor monitors SnapMirror relationships of a NetApp cDOT or ONTAP storage system accessing the application programming interface (API) via the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP).
For a detailed list and descriptions of the channels that this sensor can show, see section Channel List.
- Dutch: NetApp SnapMirror
- French: NetApp SnapMirror
- German: NetApp SnapMirror
- Japanese: NetApp SnapMirror
- Portuguese: NetApp SnapMirror
- Russian: NetApp SnapMirror
- Simplified Chinese: NetApp SnapMirror
- Spanish: NetApp SnapMirror
Consider the following remarks and requirements for this sensor:
Remark |
Description |
|---|---|
Enabled ONTAPI access |
The ONTAPI user account that you use with this sensor requires access to the DATA ONTAP API (ONTAPI) so that the sensor can request data from it. The access is enabled by default.
services web> modify -vserver clusterd -name ontapi -enabled true For this sensor, read-only user rights are sufficient for the ONTAPI user account that you use to access ONTAPI. Modify or add this user with a suitable role in the console under Cluster | ClusterX | Configuration | Security | Users |
Microsoft .NET Framework |
This sensor requires .NET 4.7.2 or later from Microsoft on the probe system. In a cluster, install it on every cluster node.
|
NetApp versions |
This sensor supports NetApp cDOT as of version 8.3 and NetApp ONTAP as of version 9.0. |
IPv6 |
This sensor supports IPv6. |
Performance impact |
This sensor has a very low performance impact. |
Credentials |
You can define NetApp API credentials (User Name and Password) in the credentials for Windows systems settings of the parent device. This way, you do not need to individually enter credentials for each NetApp sensor that you add to the same device. |
Lookups |
This sensor uses lookups to determine the status values of one or more channels. |
The sensor has the following default tags that are automatically predefined in the sensor's settings when you add the sensor:
- cdot
- netapp
- ontap
- soap
For more information about basic sensor settings, see section Sensor Settings.
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
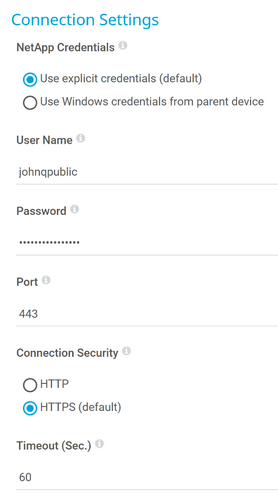
NetApp Credentials |
Specify which credentials you want to use to connect to the NetApp API:
|
User Name |
This setting is only visible if you select Use explicit credentials (default) above. Enter a user name for access to the NetApp API. Enter a string.
|
Password |
This setting is only visible if you select Use explicit credentials (default) above. Enter the password of the user for access to the NetApp API. Enter a string. |
Port |
Enter a port number on which you can access the NetApp API. Enter an integer. The default port is 443. |
Connection Security |
Define if the connection to the NetApp API is Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)/Transport Layer Security (TLS) secured:
|
Timeout (Sec.) |
Enter a timeout in seconds for the request. Enter an integer. The maximum timeout value is 900 seconds (15 minutes).
|
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
SnapMirrors |
The SnapMirror that this sensor monitors. |
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Result Handling |
Define what PRTG does with the sensor result:
|
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Primary Channel |
Select a channel from the list to define it as the primary channel. In the device tree, PRTG displays the last value of the primary channel below the sensor's name. The available options depend on what channels are available for this sensor.
|
Graph Type |
Define how this sensor shows different channels:
|
Stack Unit |
This setting is only visible if you select Stack channels on top of each other above. Select a unit from the list. PRTG stacks all channels with this unit on top of each other. By default, you cannot exclude single channels from stacking if they use the selected unit. However, there is an advanced procedure to do so. |
By default, all of these settings are inherited from objects that are higher in the hierarchy. We recommend that you change them centrally in the root group settings if necessary. To change a setting for this object only, click ![]() under the corresponding setting name to disable the inheritance and to display its options.
under the corresponding setting name to disable the inheritance and to display its options.
For more information, see section Inheritance of Settings.
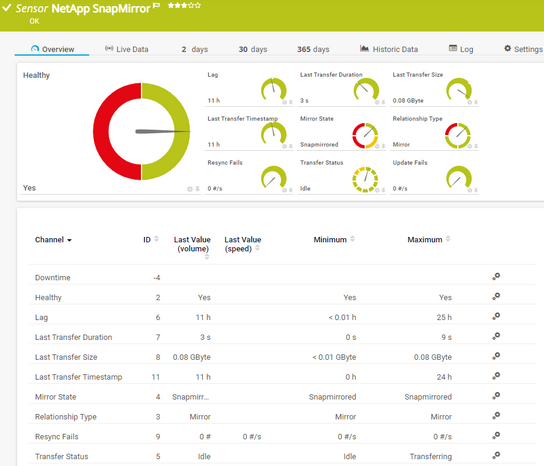
Which channels the sensor actually shows might depend on the target device, the available components, and the sensor setup.
Channel |
Description |
|---|---|
Downtime |
In the channel table on the Overview tab, this channel never shows any values. PRTG uses this channel in graphs and reports to show the amount of time in which the sensor was in the Down status. |
Healthy |
If the system is healthy
|
Lag |
The lag transfer duration |
Last Transfer Duration |
The last transfer duration |
Last Transfer Size |
The last transfer size |
Last Transfer Timestamp |
The time stamp of the last transfer |
Mirror State |
The mirror status
|
Relationship Type |
The relationship type
|
Resync Fails |
The number of resynchronization fails |
Transfer Status |
The transfer status (relationship status returned from the API)
|
Update Fails |
The number of update fails |
KNOWLEDGE BASE
Which .NET version does PRTG require?
What security features does PRTG include?