PRTG Manual: SSH Remote Ping Sensor
Important Notice |
|---|
This sensor type is deprecated. The sensor still works but you cannot add it anew as of PRTG 25.x.108. We plan to migrate and discontinue this sensor type in a future version of PRTG. We recommend that you use the SSH Remote Ping v2 sensor instead. For more information about sensor migration, see the Knowledge Base: What is a sensor migration?. |
The SSH Remote Ping sensor remotely monitors the connectivity between a system running Linux/macOS X and another device, using Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo requests ("ping") and Secure Shell (SSH).
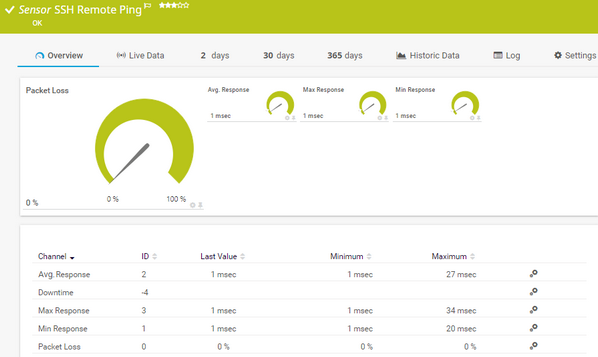
For a detailed list and descriptions of the channels that this sensor can show, see section Channel List.
- Dutch: SSH Remote Ping
- French: Ping distant (SSH)
- German: SSH Remote Ping
- Japanese: SSH リモート Ping 実行
- Portuguese: Ping remoto (SSH)
- Russian: Удаленный пинг по SSH
- Simplified Chinese: SSH 远程 Ping
- Spanish: Ping remoto (SSH)
Consider the following remarks and requirements for this sensor:
Remark |
Description |
|---|---|
Performance impact |
This sensor has a high performance impact. We recommend that you use no more than 200 of this sensor on each probe. |
Credentials |
This sensor requires credentials for Linux/Solaris/macOS (SSH/WBEM) systems in the settings of the parent device. |
Distributions |
This sensor does not support all Linux/Unix and macOS distributions. |
IPv4 |
This sensor only supports IPv4. |
Knowledge Base |
|
The sensor has the following default tags that are automatically predefined in the sensor's settings when you add the sensor:
- pingsensor
- remotepingsensor
- sshremotepingsensor
For more information about basic sensor settings, see section Sensor Settings.
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Target |
Enter the Domain Name System (DNS) name or IP address of the target device the ping is sent to. The sensor remotely connects to the parent device it is created on via SSH, then performs a ping request from this remote device to the target device or server. Enter a string. |
Packet Size (Bytes) |
Enter the packet size for the ping in bytes. You can enter any value between 1 and 10000. Enter an integer.
|
Packet Count |
Enter the number of packets that the sensor sends with each scanning interval. |
Custom Parameters |
Optionally, enter additional parameters that the sensor adds at the end of the ping command. Enter a string or leave the field empty.
|
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Connection Timeout (Sec.) |
Define a timeout in seconds for the connection. This is the time that the sensor waits to establish a connection to the host. Keep this value as low as possible. The maximum timeout value is 900 seconds (15 minutes). Enter an integer.
|
Shell Timeout (Sec.) |
Define a timeout in seconds for the shell response. This is the time in seconds the sensor waits for the shell to return a response after it has sent its specific command (for example, cat /proc/loadavg). The maximum value is 300 seconds (5 minutes). Enter an integer.
|
SSH Port Inheritance |
Define which port this sensor uses for the SSH connection:
|
Custom SSH Port |
This setting is only visible if you select Do not inherit port (enter a custom SSH port) above. Enter the port number (between 1 and 65535) that this sensor uses for the SSH connection. Enter an integer. |
SSH Engine |
Select the SSH engine that you want to use to access data with this SSH sensor:
|
Result Handling |
Define what PRTG does with the sensor result:
|
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Primary Channel |
Select a channel from the list to define it as the primary channel. In the device tree, PRTG displays the last value of the primary channel below the sensor's name. The available options depend on what channels are available for this sensor.
|
Graph Type |
Define how this sensor shows different channels:
|
Stack Unit |
This setting is only visible if you select Stack channels on top of each other above. Select a unit from the list. PRTG stacks all channels with this unit on top of each other. By default, you cannot exclude single channels from stacking if they use the selected unit. However, there is an advanced procedure to do so. |
By default, all of these settings are inherited from objects that are higher in the hierarchy. We recommend that you change them centrally in the root group settings if necessary. To change a setting for this object only, click ![]() under the corresponding setting name to disable the inheritance and to display its options.
under the corresponding setting name to disable the inheritance and to display its options.
For more information, see section Inheritance of Settings.
Which channels the sensor actually shows might depend on the target device, the available components, and the sensor setup.
Channel |
Description |
|---|---|
Avg. Response |
The average response time measured from the remote device |
Downtime |
In the channel table on the Overview tab, this channel never shows any values. PRTG uses this channel in graphs and reports to show the amount of time in which the sensor was in the Down status. |
Max. Response |
The maximum response time measured from the remote device |
Min. Response |
The minimum response time measured from the remote device |
Packet Loss |
The packet loss (%)
|
KNOWLEDGE BASE
Which encryption algorithms do PRTG SSH sensors support?
SSH and SFTP sensors in Unknown status
What security features does PRTG include?
How do I set up SSH sensors with my AWS Linux instances?