IoT World
What is LPWAN?
LPWAN stands for Low-Power Wide-Area-Network. It does not refer to any one specific technology, but rather serves as a generic term for any network designed to communicate wirelessly with lower power than other networks such as cellular, satellite, or WiFi. Moreover, LPWANs communicate over greater distances than other low-power networks that use Bluetooth or NFC.
Typically, communicating over long distances with low power allows less data to be transmitted at a time. Whereas modern cellular networks are pushing into gigabit per second territory with LTE Advanced and the forthcoming 5G networks, LPWA networks often transmit just a few kilobits per channel. Many LPWA technologies can communicate over greater distances, sometimes up to 500 miles or more.
LPWAN transceivers, Sigfox and overlaps with IIoT
LPWAN transceivers
There are essentially two approaches that make the high sensitivity of LPWA possible. On the one hand, virtually all systems are narrow-banded. LPWA can therefore be used to achieve a high coverage in communication.
Secondly, the net data rates are low, so that a lot of energy per bit can be integrated. LPWA is an extremely energy-efficient way of communication, far more economical than other standards currently in use.
The combination of range and required energy makes LPWA an unparalleled transmission path.
What is Sigfox?
Sigfox sets up its own global wireless network to wirelessly connect low-power objects to the Internet. Sigfox provides its modules and terminals at very competitive prices, and the use of the Sigfox infrastructure is cost-effective and flexible.
The infrastructure used is completely independent of existing networks, such as mobile phone networks. Currently, a total of 65 countries and regions are either fully or partially covered.
The aim of Sigfox is to establish a worldwide, uniform network structure via its own network, which focuses on the networked object and its data.
LPWAN and IIoT
Wireless-data transmission systems are the ideal starting point for intelligent devices and machines in product manufacturing. Here we are entering the IIoT sector, which is the industrial version of IoT.
While IoT usually combines applications from other customer segments, such as Smart City or Smart Home, IIoT is all about networking objects or work equipment.
This makes it possible to automatically analyze, monitor and optimize various processes. Since equipment in larger industries has a high purchase price, LPWAN offers a very broad potential market because it is easier to retrofit.
Here are just a few examples of a widely used LPWA network
Parking management
A sensor in or near an urban parking spot can report whether the spot is occupied or not. The data can then be used to feed numerous applications including signs that show how many open parking spots are available on a parking garage level. The low power aspect in particular comes into play here. A Smart City must be sustainable and cleverly designed, with as little maintenance as possible.
Water meters & pipelines
A simple pressure meter communicating its current reading can help pinpoint a leak even before it is reported. For pipelines that stretch over miles, the ability to communicate over long distances without an existing network is critical, and battery life needs to be measured in years. In a city, the same signal that provides long-distance communication in a rural environment can instead provide underground communication.
Smart pallets
Tracking shipments typically requires that cargo is scanned at every point that it changes hands. Between these changes, it is assumed that the cargo is still in the same building, or when on the move, in the same truck or train. With a smart pallet, a ping can continuously update not only the location, but also whether the container has been dropped, opened, or otherwise mishandled.
Street & highway lighting
Our world can't live without electric light (just take a look at NASA footage of an earth night). Currently, monitoring often consists of someone noticing a problem and making a phone call. With LPWA, these lights can let a central command center know if the bulb is working, or if the light is currently on, allowing for better energy usage and increased safety. It also potentially allows traffic control, which can improve air quality in urban areas.
Other uses include smart meters, as well as smart agriculture, and factory and warehouse sensors.
Monitor your devices with PRTG and Sigfox
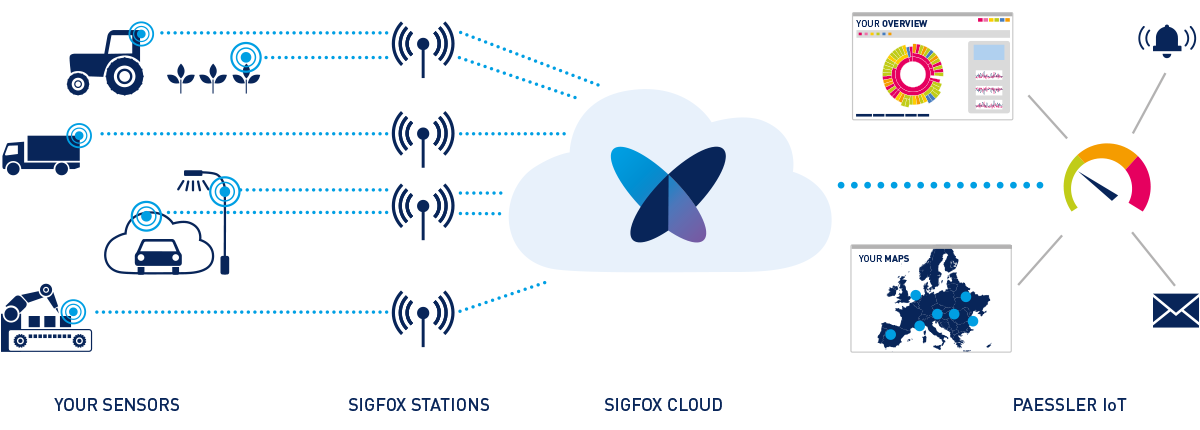
LPWAN sensors require little infrastructure or energy, and no WLAN or cabling.
Simply attach the sensor on site or on the device to be monitored and it sends measurement data, such as geo location (independent of GPS,
also indoors), acceleration, temperature, air quality, soil quality, humidity etc., via the Sigfox network to the Sigfox server (Sigfox Cloud).
The Sigfox backend provides data as a callback or via API. TIP: Decode Payloads via Paessler BitDecoder
Why monitoring?
LPWA technologies have already achieved an impressively strong market position in just a few years. This development will continue for years to come, even though more and more technologies are entering the market. At Paessler, we really believe that we have a crucial market ahead of us in LPWA, which will become the connection standard of IoT.
The potential of a technology such as LPWAN is enhanced by good monitoring. It should be possible to measure typical sensor data coming from LPWAN devices. It should also be possible to monitor a factor such as geolocation, i.e. the geographical information of a device. Finally, additional information about an LPWAN device should be available with a typical cloud solution and REST API.

Case study
We at Paessler have understood the potential that lies in LPWAN, and although we are dealing with a still-developing branch of technology (at least as far as the broad application of LPWAN in the context of IoT is concerned), we can already show some very detailed use cases.
In this video we illustrate how the connection of PRTG and Sigfox looks in a practical application case. Our cooperation with the National Museum of Computing in the famous Bletchley Park is based on this use case.
If you are interested, take a look at our other activities at the The National Museum of Computing.
Want to start
monitoring with PRTG?
In this tutorial video, we show you how to monitor Sigfox data with PRTG.

Although we at Paessler have entered into a strategic partnership with Sigfox and we write a lot about Sigfox,
this does not mean that other standards cannot also be monitored with PRTG. On the contrary.
We are already developing potential use cases with MIOTY from the Frauenhofer Institute and the long range (LoRa) technology.



