O SNMP é uma das tecnologias mais comumente usadas quando se trata de monitoramento de rede.
Programas de monitoramento de largura de banda como o Paessler PRTG o utilizam.
Mas como o SNMP funciona?
MIB significa Management Information Base (Base de informações de gerenciamento) e é uma coleção de informações organizadas hierarquicamente. Elas são acessadas por meio de um protocolo como o SNMP. Há dois tipos de MIBs: escalar e tabular.
Os objetos escalares definem uma única instância de objeto, enquanto os objetos tabulares definem várias instâncias de objeto relacionadas, agrupadas em tabelas MIB.
As MIBs são coleções de definições que definem as propriedades do objeto gerenciado dentro do dispositivo a ser gerenciado.
Exemplo de MIB: Os objetos típicos a serem monitorados em uma impressora são os diferentes estados do cartucho e talvez o número de arquivos impressos; em um switch, os objetos típicos de interesse são o tráfego de entrada e saída, bem como a taxa de perda de pacotes ou o número de pacotes endereçados a um endereço de broadcast.
OIDs significa Object Identifiers (identificadores de objetos). Os OIDs identificam exclusivamente os objetos gerenciados em uma hierarquia MIB. Isso pode ser representado como uma árvore, cujos níveis são atribuídos por diferentes organizações. Os OIDs (Object IDs) de nível superior do MIB pertencem a diferentes organizações padrão.
Os fornecedores definem ramificações privadas, incluindo objetos gerenciados para seus próprios produtos.
Aqui está um exemplo de estrutura de um OID:
ou apenas:
Esses números SNMP OID são os usados no PRTG ao configurar sensores customizados, a fim de acessar os elementos apropriados do dispositivo que se deseja monitorar. Os OIDs são geralmente fornecidos pelos fabricantes de hardware ou podem ser encontrados nos chamados repositórios OID, onde coleções de árvores MIB e os respectivos OIDs podem ser acessados.
O PRTG lê esses OIDs e os atribui ao dispositivo pertinente, monitorando respectivamente o dispositivo selecionado e seu OID específico. Mais informações sobre o PRTG...
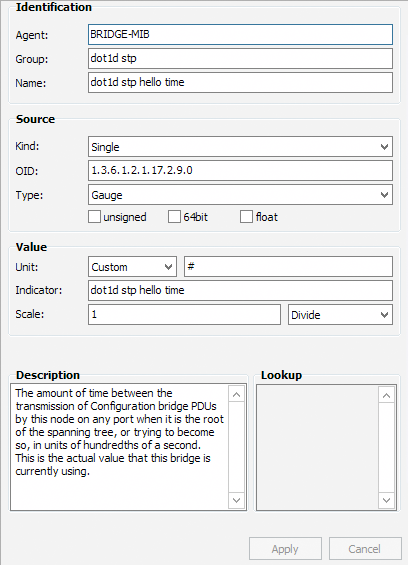
Propriedades de um OID
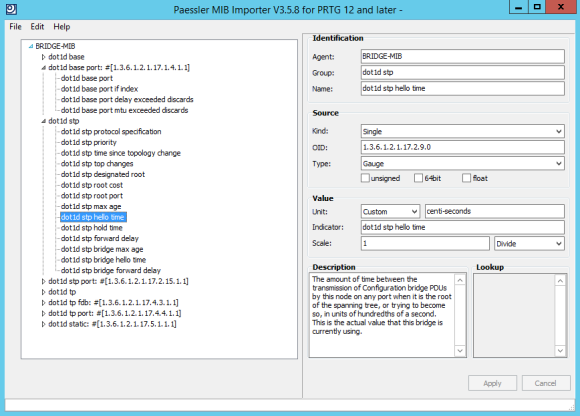
Biblioteca OID aberta no importador MIB
As notificações em tempo real significam uma solução de problemas mais rápida para que você possa agir antes que ocorram problemas mais sérios.
SNMP é a sigla de Simple Network Management Protocol (Protocolo Simples de Gerenciamento de Rede). Sua utilidade na administração de redes se deve ao fato de permitir a coleta de informações sobre dispositivos conectados à rede de forma padronizada em uma grande variedade de tipos de hardware e software. O SNMP é um protocolo para transferência de informações de gerenciamento em redes, especialmente para uso em LANs, dependendo da versão escolhida.
O SNMP versão 1, que é o padrão SNMP suportado pelo PRTG, foi o desenvolvimento inicial do protocolo SNMP. Uma descrição pode ser encontrada na Request for Comments (RFC) 1157 e funciona dentro da especificação da Structure of Management Information (SMI).
Ele opera com User Datagram Protocol (UDP), Internet Protocol (IP), OSI Connectionless Network Services (CLNS), AppleTalk Datagram Delivery Protocol (DDP) e Novell Internet Packet Exchange (IPX). O SNMP v1 é considerado o protocolo de gerenciamento de rede de fato na comunidade da Internet.
O SNMP funciona com base no fato de que os sistemas de gerenciamento de rede enviam uma solicitação e os dispositivos gerenciados retornam uma resposta. Isso é implementado por meio de uma das quatro operações: Get, GetNext, Set e Trap. As mensagens SNMP consistem em um cabeçalho e uma PDU (unidades de dados de protocolo). Os cabeçalhos consistem no número da versão do SNMP e no nome da comunidade. O nome da comunidade é usado como uma forma de segurança no SNMP. A PDU depende do tipo de mensagem que está sendo enviada. Os campos Get, GetNext e Set, bem como a PDU de resposta, consistem em tipo de PDU, ID de solicitação, status de erro, índice de erro e objeto/variável. O Trap consiste nos campos Enterprise, Agent, Agent address, Generic trap type, Specific trap code, Timestamp e Object/Value.
Os MIBs são uma coleção de definições que definem as propriedades do objeto gerenciado dentro do dispositivo a ser gerenciado (como um roteador, switch etc.). Cada dispositivo gerenciado mantém um banco de dados de valores para cada uma das definições escritas no MIB. Dessa forma, não se trata, de fato, de um banco de dados, mas de uma dependência da implementação. Cada fornecedor de equipamentos SNMP tem uma seção exclusiva da estrutura de árvore MIB sob seu controle.
Para que tudo isso seja organizado adequadamente, todos os recursos gerenciáveis de todos os produtos (de cada fornecedor) são organizados nessa árvore. Cada "ramo" dessa árvore tem um número e um nome, e o caminho completo do topo da árvore até o ponto de interesse forma o nome desse ponto. Esse é o OID. Os nós próximos ao topo da árvore são de natureza extremamente geral. Por exemplo, para acessar a Internet, é preciso chegar à quarta camada. À medida que se desce, os nomes se tornam cada vez mais específicos, até chegar à base, onde cada nó representa um recurso específico em um dispositivo (ou agente) específico.
O PRTG é um software abrangente de monitoramento de rede e mantém o controle de toda a sua infraestrutura de TI.
Esse software de monitoramento de rede baseado em Windows e o serviço ASP multiplataforma tornam fácil e acessível a detecção precoce de falhas na rede e no site, minimizando o tempo de inatividade e evitando o impacto econômico. O monitor de servidor ajuda as organizações a monitorar os recursos críticos da rede e a detectar imediatamente falhas no sistema ou problemas de desempenho. Freeware disponível! Mais...